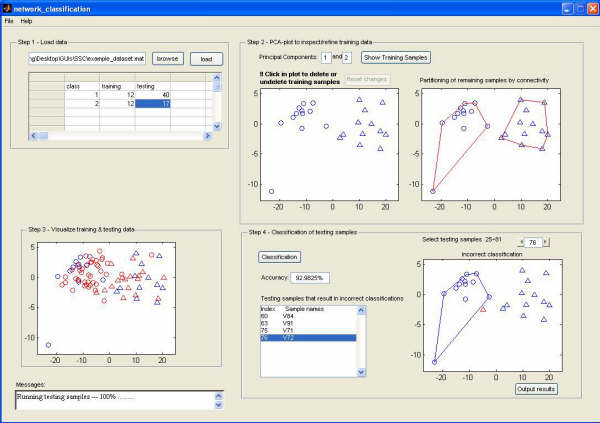
3. Spectral Analysis for Class Discovery and Classification (SPACC)
Classification methods are mainly divided into two categories. Unsupervised methods do not use class labels. They have the ability to discover new classes, but lack ways to identify new classes systematically. In supervised methods, the class label information plays such an important role that supervised methods do not have the ability to discover new classes. I developed a novel classification method, SPACC, where the key idea is to make the class label information play a less important role. SPACC is the first that performs class discovery and classification simultaneously.
The software can be downloaded
here
4. Fast Calculation of Pairwise Mutual Information Based on Kernel Estimation
We present a new software implementation for more efficiently computing the mutual information for all pairs of genes from gene expression microarrays. Computation of the mutual information is a necessary first step in various information theoretic approaches for reconstructing gene regulatory networks from microarray data. When the mutual information is estimated by kernel methods, computing the pairwise mutual information is quite time-consuming. Our implementation significantly reduces the computation time. For an example data set of 9563 genes and 336 samples, the current available software for ARACNE requires 142 hours to compute the mutual information between all possible pairs of genes, whereas our implementation requires 1.6 hours.
The Matlab code is available at here
5. TreeVis: A MATLAB-based Tool for Tree Visualization
Many analyses of biological data produce results in the form of tree structures. Generating easily interpretable layouts to visualize these tree structures is a non-trivial task. We present a new visualization algorithm, TreeVis, to generate clear two-dimensional layouts of complex tree structures.
The Matlab code is available at
here